A CredSpark Deep Dive
The CredSpark Beginner’s
Guide to Audience Data
Chapter One:
An Intro to Sparking Successful Audience Engagement
What is audience data?
Audience data refers to the collection of information about the users and/or consumers of a product, service, or content. This encompasses a wide range of types of data such as demographics, psychographics, behaviors, and engagement patterns. Audience data is gathered through various channels that serve to better inform overall strategy. The primary purpose of audience data is to gain data-driven insights into who the audience is, what they prefer, and what drives their decisions. This is invaluable intelligence for businesses and aids in tailoring strategies for content, product development, marketing, R&D, and more.
Why is audience data important?
Audience data enhances targeting and personalization, while improving customer experience and guiding effective content strategies. It enables informed decision-making which leads to increased return on investment in marketing and other business initiatives. By providing insights into customer preferences, behaviors, and demographics, audience data provides competitive advantage, helps identify market trends, qualifies potential sales leads, assesses audience knowledge, and generates insights into how to improve products and services. Audience data is essential to developing a cohesive cross-channel marketing strategy and building flourishing customer relationships. Ultimately, data is key to adapting to the ever-changing landscape of audience needs, goals, and interests.
Key Terms to Know: CredSpark’s Audience Data Glossary
Audience data is the comprehensive collection of information about the individuals that are interacting with your brand. Understanding audience data allows you to learn about the people who are responding to your ads, buying your products, and interacting with your content. There are six main types of Audience Data. Let’s take a look.
Demographic Data
Demographic data consists of socioeconomic information, typically including employment, education, income, age, and gender – basic attributes that help you paint a broader picture of your audience.
Psychographic Data
Psychographic data typically includes information about a person’s values, attitudes, personality traits, and overall interests. It delves deeper, finding out what specific triggers motivate your audience to take an action. Effective use of psychographic data can help you better target your messaging based on what drives your audience to take action.
Intent Data
Intent data reveals online behaviors signaled from your target audience. Whether they are intending to purchase your product, subscribe to your content, or switch to a competitor, intent data helps you detect these signals and allows you to stay ahead of the curve.
Interest Data
Interest data is for actionable use by customer service, marketing, and sales teams. By using methods like interactive content, companies are able to derive audience interest data from the choices they make, feedback they provide, and help paint an overall picture of who exactly your customers are.
Firmographic Data
Firmographic data provides intelligence and insights for organizations or firms. This type of data collects and analyzes key organizational information, including industry type, organizational size, total sales & revenue, current location, ownership structure, and growth trends.
Behavioral Data
Behavioral data is generated from customer engagement with businesses or organizations. In the digital landscape, this looks like page views, video views, e-commerce transactions, downloads, heat maps, and scroll maps. Collecting behavioral data is extremely important for marketers to understand user activity and trends and where to target their efforts in user experience, advertising, product development, and more.
Declarative Data
Declarative data, or Zero-Party Data, is data which consumers and audience members self-report. Not only is it extremely straightforward, declarative data is an efficient solution for consumer behavior analysis and creating a better understanding of your audience, customers, and communities.
Passive Data
Passive data is data collected without participation of the people directly involved in the process. The best use case for passive data is for assessment and problem solving. Typically this is collected through a computer tracking system and automatically recorded.
Zero-Party Data (ZPD)
Zero-Party Data is information that a person intentionally shares with a business or organization. It includes preferences, personal context, purchase intent, and more. The term refers to the fact that there are zero steps between the collector and the data source.
First-Party Data (FPD)
Zero-Party Data is information that a a business or organization collects directly from its audience through interactions with its brands. It includes sales history, registrations, social media interactions, online behavior tracking, and more.
Second-Party Data (SPD)
Second-Party Data is information that is collected by another organization and shared or sold to the user of that information.
Third-Party Data (TPD)
Third-Party Data is information that is collected and packaged—without a direct connection to the people it’s attached to— by external data providers like public records, government information, market research companies and more.
The Collection of Audience Data
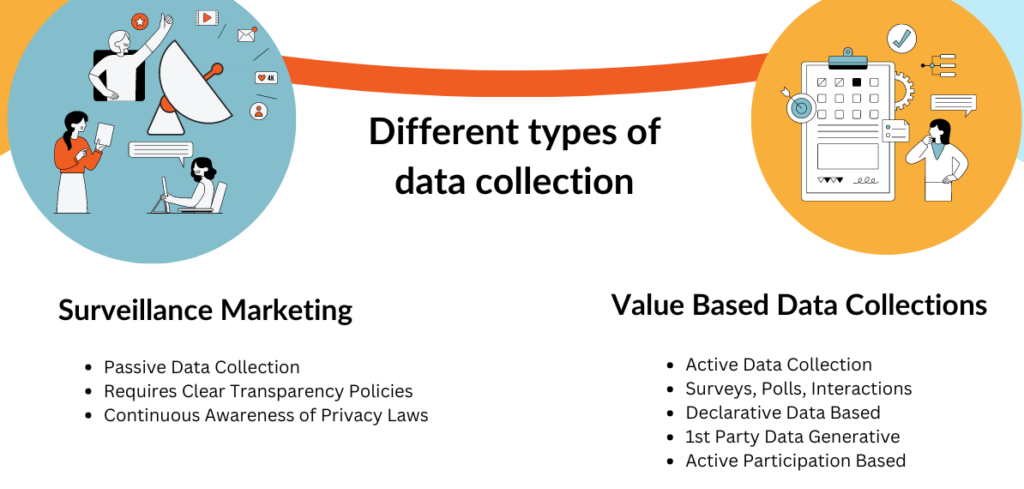
There are two different ways to collect audience data. The two types of data are very different in form and use cases, but are typically used for the same purpose: to guide business decisions and improve outcomes.
Surveillance Marketing
Surveillance marketing occurs subtly through methods like cookies, tracking pixels, links, and website analytics to collect information about user behavior. Behavioral data plays a pretty big role in the surveillance marketing process. The key best practice to remember with surveillance marketing is being transparent about your practices and respect user privacy. The term “surveillance” suggests how disconcerting individuals can find these practices. Transparency involves explicitly stating what data you’ll be collecting and how you’ll use it.
Value-Based Data Collection
Value-based data collection takes a different approach. Using methods like surveys, polls, and other interactions, you’re able to pose specific questions that generate insights directly from your audience. These kinds of data collection methods are directly linked to declarative data, which is always collected through methods previously listed when the participant is actively participating and giving feedback. Additionally, the transparency of value-based data collection builds trust with your brand.
Dive Deeper: 3 Methods of Audience Data Collection
Align audience data with your business objectives.
Before you start looking for data, you should understand how you’ll be using it. A comprehensive data strategy helps you identify what you need, how you’ll use it, and surface the best methods for collecting it. Surveillance marketing and value-based data collection have very different methodologies, so you’ll want to be deliberate in your choice of which to use.
Define your objectives.
Before you go all-in on your data collection efforts, make sure your data strategy is clearly aligned with your business’ overall objectives. Whether it’s sales growth, audience knowledge, lead generation, market research or more, define what audience information you need and develop a strategy on how to collect over time.
Identify key metrics.
To monitor performance in the right areas, define the metrics you need to track. The amount of data being generated can be overwhelming; so it’s important to focus on what will truly provide the insights you need to move the needle on your objectives.
Think about data integration.
The key considerations for data integration are:
- How will you store it?
- For how long?
- Will it be secure?
- And how can decision makers access it and surface the insights they need?
Whether you’re using a commercial platform or a in-house system, the ability to access, analyze, and report on the data you collect is essential to an effective Audience Data Strategy.
Dive Deeper: A Progressive Approach to Audience Data
Audience data drives new opportunities.
Think of audience data as an asset of your business. Assets can be deployed in multiple ways to drive new business opportunities. Here are three examples of top use cases for audience data that we often see at CredSpark.
Advertising, Lead Generation, Precision Marketing & Sales Support
Actionable information opens up countless data-driven opportunities to grow a business. From advertisers and sponsors to internal marketing and sales teams, high-quality market intelligence can enhance and enrich a wide range of business objectives. A comprehensive audience data strategy can enable hyper-qualification of leads, more precise targeting for advertising and marketing automation, and detailed intent information that sales teams can act on immediately. Audience data may not be a business operation in and of itself, however, done the right way, it can make all your other business operations a lot smarter and more effective. Look at an effective Audience Data Strategy as a force multiplier.
Long-Term Relationship Building
Beyond transactional opportunities, the insights derived from collecting audience data can help you make more meaningful connections with your audience. With more insight into their preferences, interests, needs, and goals, you’ll have countless opportunities to create more value for them, including creating content, interactions, products, services and more that are all more aligned to their needs.
In addition, audience data allows you to build richer profiles of each audience member. By collecting data progressively over time, you can track even subtle changes in market conditions and audience needs and ensure you are reacting accordingly. And to bring it full circle, acting on this real-time intelligence deepens your relationships with your various audiences (customers, leads, sponsors, employees, etc.) and that in turn, drives better outcomes for traditional business metrics (sales, subscriptions, positive reviews, churn rate, time on site, and more).
Personalization
Creating tailored experiences can be hard without the right tools, But if you gather any audience data, you can craft content that speaks directly to your audience’s preferences, interests, and needs. When customers get tailored recommendations and attention that aligns with their tastes, they are more likely to engage, subscribe, make purchases, and return for more.
Use your audience data to drive content recommendations that cater to specific interests and behavior. If you can suggest the right content, products, and services, they’ll spend more time on your site, explore more areas of interest, and hopefully help you reach your goals more effectively and organically.
If you leverage personalization correctly, you build authentic connections with your audience, and enhance your engagement while demonstrating that you understand and value your audience’s individuality. Audience data is the key to crafting experiences that resonate on a personal level. If you know your audience’s preferences, needs, and behaviors, you can create custom experiences that deliver value in ways that matter most to them.
Dive Deeper: Audience Data Success: 5 Examples
Bringing It All Together
Now that you know what audience data is, take some time and dive deeper into CredSpark’s Beginner’s Guide to Audience Data and learn how to collect it more effectively, experience successful examples and use cases, and even test what you’ve learned.








